
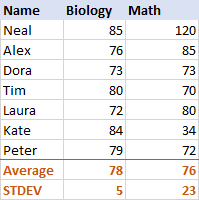
For instance, a search of Google Scholar on Novemshowed that the article of Hozo et al.’s method has been cited 722 times where 426 citations are made recently in 20. Their method is now widely accepted in the literature of systematic reviews and meta-analysis. They proposed a simple method for estimating the sample mean and the sample variance (or equivalently the sample standard deviation) from the median, range, and the size of the sample. were the first to address this estimation problem. Therefore, we need to estimate the sample mean and standard deviation from these quantities so that we can pool results in a consistent format.
#TOTAL MEAN AND STANDARD DEVIATION EXCEL TRIAL#
Specifically in medical research, instead of reporting the sample mean and standard deviation of the trials, some trial studies only report the median, the minimum and maximum values, and/or the first and third quartiles. This, however, can be difficult because results from different studies are often presented in different and non-consistent forms.

In meta-analysis of continuous outcomes, the sample size, mean, and standard deviation are required from included studies. With the combination of several studies and more data taken into consideration in systematic reviews, the accuracy of estimations will get improved and more precise interpretations towards the treatment effect can be achieved via meta-analysis. The methodology in systematic reviews is usually referred to as meta-analysis.
Systematic reviews use specific and explicit criteria to identify and assemble related studies and usually provide a quantitative (statistic) estimate of aggregate effect over all the included studies. Hence, from the mid-1980s, systematic reviews and meta-analysis have become an imperative tool in medical effectiveness measurement. To claim a treatment effect, different reviewers may use different thresholds, which often lead to opposite conclusions from the same study. The major one is due to inconsistent criteria of different reviewers. However, this approach suffers from many critical flaws. Prior to the 1990s, the traditional approach to combining results from multiple trials is to conduct narrative (unsystematic) reviews, which are mainly based on the experience and subjectivity of experts in the area.
pointed out that systematic reviews and meta-analysis of randomized control trials would have led to earlier recognition of the benefits of thrombolytic therapy for myocardial infarction and may save a large number of patients. While individual trial study could fail to show a statistically significant treatment effect, systematic reviews and meta-analysis of combined results might reveal the potential benefits of treatment. In medical research, it is common to find that several similar trials are conducted to verify the clinical effectiveness of a certain treatment.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
